Track 01: Urban Planning AI
Overview
Urban Planning AI is the process of plan-making that is conducted, either partially or entirely, by an AI agent during the urban planning process. Specifically, an Urban Planning AI agent can encompass various computer programs or systems created to assist or automate different tasks involved in the planning process, similar to ChatGPT, enabling planners to make more informed and effective decisions (Peng et al, 2023). With different levels of AI involvement in the planning process, urban planning AI spans from initial AI-assisted plan-making to fully automated plan-making:
Research Project
| Dissertation: AI-Driven Approach to Optimize and Automate Shared Micromobility System Planning and Operation |
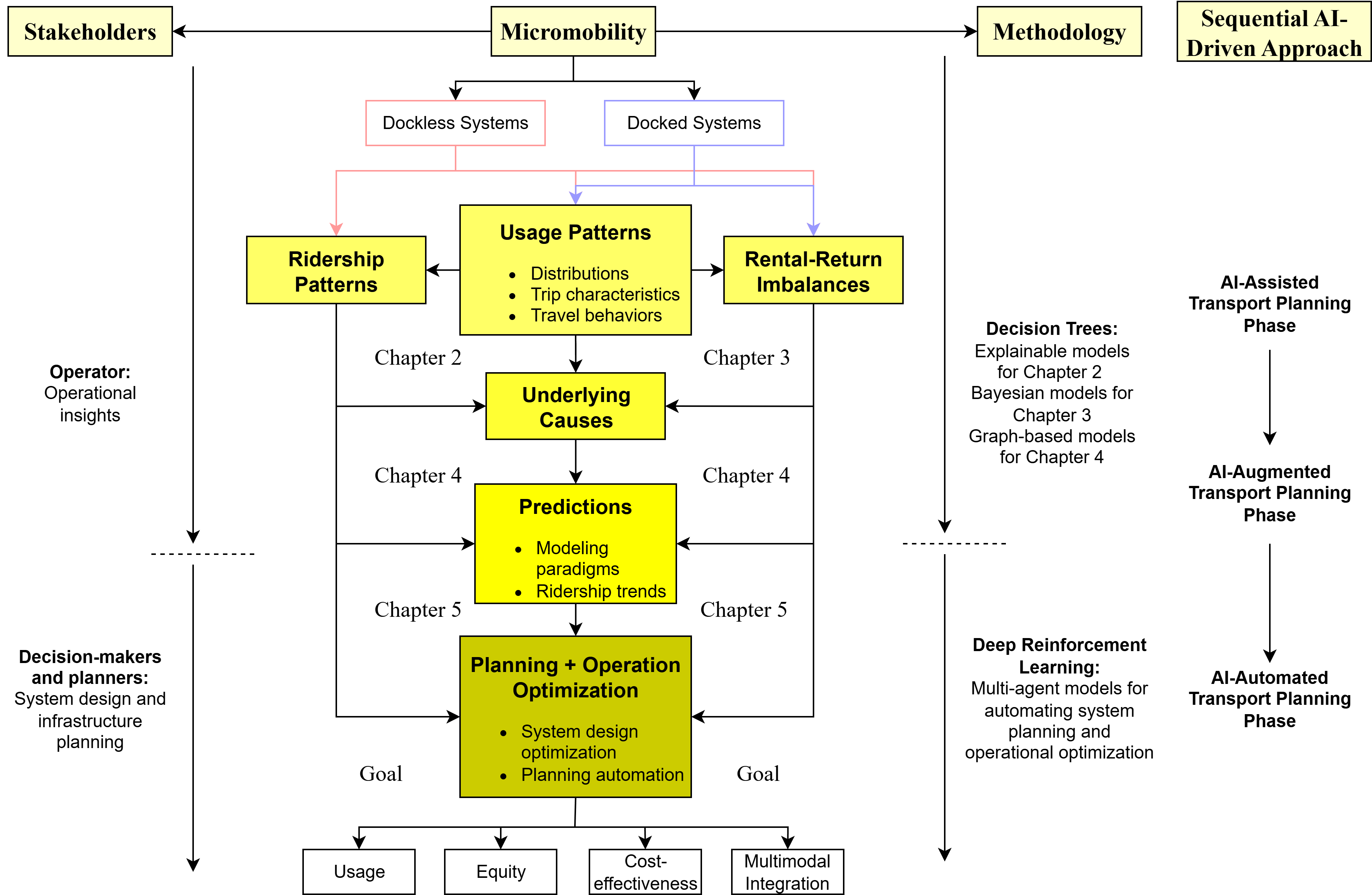 |
Publications
Journal Papers
- Lu, K., Hou, Q., Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., Peng, Z. (2025). Planning Automation of Shared Micromobility System Design: A Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. Nature Computational Science. (Under Review)
- Peng, Z., Lu, K., Liu, Y., Hou, Q., Zhang, Q. (2025). AI-Human Co-Creation in Urban Planning: The CORE Framework for Symbiotic Planning Theory. Journal of the American Planning Association. (Under Review)
- Lu, K., Peng, Z. (2025). AI-Driven Approach to Optimize and Automate Shared Micromobility System Planning and Operation (Dissertation). University of Florida
- Peng, Z., Lu, K., Liu, Y., & Zhai, W. (2024). The Pathway of Urban Planning AI: From Planning Support to Plan-Making. Journal of Planning Education and Research, 44(4), 2263-2279 [Text].
- Liu, Y., Peng, Z., Hou, Q., & Lu, K. (2024). The Role, Opportunities, and Challenges of Generative AI in Comprehensive Planning of American Small Towns – Using ChatGPT as an Example (in Chinese). Journal of Urban Regional Planning, 16(1), 215-228.
- Lu, K., Liu, Y., Peng, Z., Zhai, W. (2025). Evaluating and Predicting Transportation Network Performance Resilience to Extreme Weather Events: A Spatiotemporal Multi-Graph Diffusion Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (ST-MGDCRNN) Approach. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (T-ITS). (Under Review)
- Miao, C., Peng, Z., Cui, A., He, X., Chen, F., Lu, K., … & Chen, W. (2024). Quantifying and Predicting Air Quality on Different Road Types in Urban Environments Using Mobile Monitoring and Automated Machine Learning. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 15(3), 102015 [Text].
- Wang, D., Wang, H., Lu, K., et al. (2022). Regional Prediction of Ozone and Fine Particulate Matter Using Diffusion Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 3988 [Text].
- Wang, D., Wang, H., Li, C., Lu, K., et al. (2020). Roadside Air Quality Forecasting in Shanghai with a Novel Sequence-to-sequence Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9471 [Text].
Presentations & Talks
- 2025.10: Association of Collegiate Schools of Planning (ACSP) Conference. AI-Driven Approach to Optimize and Automate Shared Micromobility System Design and Planning. Minepolis, MN, USA.
- 2025.01: Transportation Research Board 104th Annual Meeting. Integrating Public Transit Effects and Street View Imagery into a Dynamic Spatiotemporal Graph-based Machine Learning Model for Predicting Bike-sharing Ridership. Washington D.C., USA.
- 2024.06: Guest Lecture at Chang’an University. Integrating Public Transit Effects and Street View Imagery into a Dynamic Spatiotemporal Graph-Based Machine Learning Model for Analyzing and Predicting Bike-Sharing Ridership. Xi’an, China
- 2024.01: Transportation Research Board 103rd Annual Meeting. Demystifying the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Rental-Return Imbalance on Bike-Sharing Systems: A Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART) Model. Washington D.C., USA.
- 2023.10: Association of Collegiate Schools of Planning (ACSP) Conference. Leveraging Deep Learning with Geospatial Data Analytics for Quantification and Prediction of Performance Resilience of Transportation Networks against Extreme Weather Events. Chicago, IL, USA.
- 2023.07: The 17th International Association for China Planning (IACP) Conference. Using Origin-Destination Flow Graph and Public Transit Information to Enhance Short-Term Ridership Prediction in Bike-Sharing Systems. Tianjin, China.
- 2023.01: Transportation Research Board 102nd Annual Meeting. Characterization and Prediction of Transportation Network Resilience: A Spatiotemporal Graph Diffusion Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Approach. Washington D.C., USA.